How to optimize your BFR

Le BFR est un indicateur de gestion qui reflète le niveau d’autonomie financière de l’entreprise. Tout dirigeant doit savoir et savoir gérer l’écart de trésorerie entre les dépenses et les revenus de son activité s’il veut anticiper et prévenir les risques à court terme. En tant qu’expert du recouvrement de créances, voici nos conseils pour optimiser votre BFR .
What is BFR? – Need funds
The Working Capital Requirement is equivalent to the permanent cash shift resulting from the company’s current activity. In other words, WCR is the result of the difference between receipts (income) and disbursements (expenses) of a company .
Indeed, when a company markets a good or a service, it must:
- First incur preliminary expenses to build up a starting stock,
- So sell them
- And finally cash in its receipts.
How to calculate the BFR?
The BFR is made up of three elements:
- The amount of the average outstanding amount of trade receivables: average of the sums invoiced to customers and not yet settled,
- The amount of the average outstanding supplier debts,
- The average amount of stocks: (initial stock + ending stock) / 2
Here is the calculation formula:
WCR = inventories + trade receivables – supplier debts.
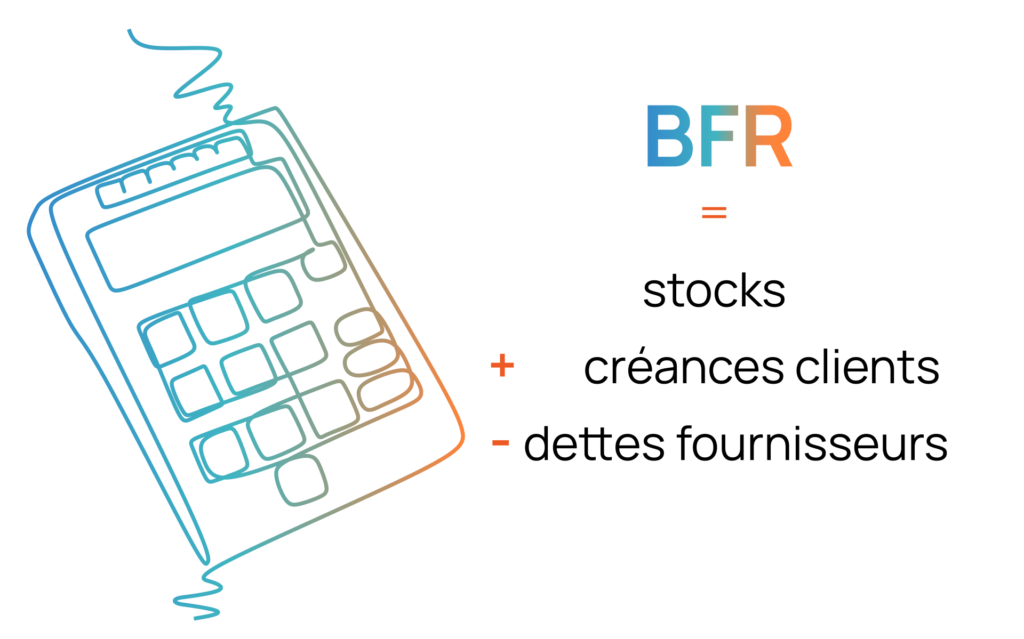
Example of calculating a BFR
A production company has the following characteristics:
– Turnover (CA) excluding taxes: €700,000
– Turnover including tax (20% VAT): €840,000
– Purchases represent 35% of turnover excluding tax, i.e. €235,200 (€294,000 including tax)
– Customer payment terms: 40% of customers pay within 30 days and 60% within 60 days.
– Terms of supplier payment: 20% of suppliers are paid within 60 days and 80% within 30 days.
– Stocks of raw materials: 1.5 months of purchases excluding tax
– Stocks of finished products: 9 days of turnover excluding VAT
The calculation of the BFR will be done as follows:
1) Stocks of raw materials:
€235,200 x 1.5 / 12 months = €29,400
2) Inventory of finished products:
€700,000 x 9 / 365 days = €17,260
3) Trade receivables:
40% x 30 days = 12 days
60% x 60 days = 36 days
That is in total: 48 days of turnover including tax (invoices are established including tax)
€840,000 x 48 / 365 days = €110,466
4) Supplier credit:
20% at 60 days = 12 days
80% at 30 days = 24 days
i.e. 36 days of purchases including tax
€294,000 x 36 / 365 days = €28,997.
WCR = (29,400 + 17,260 + 110,466) – 28,997 = €128,129
WCR: the special case of service companies
Take the example of a consulting firm that sells intellectual services. This company has no inventory of goods. These are the current charges that he must advance before being able to invoice the services which will be taken into account in the calculation of his BFR .
Thus the first stage of calculation will consist in obtaining the cost of a working day, all current charges included, salary included.
The second step will be to know the number of working days necessary to carry out the mission sold to the client.
Finally, if an order deposit is obtained for each sale, an “average customer deposit outstanding” will replace the average supplier outstanding.
The general formula for calculating the WCR of a service company will therefore be:
WCR = Work in progress + Average outstanding “Customer receivables” – Average outstanding “Customer installments”
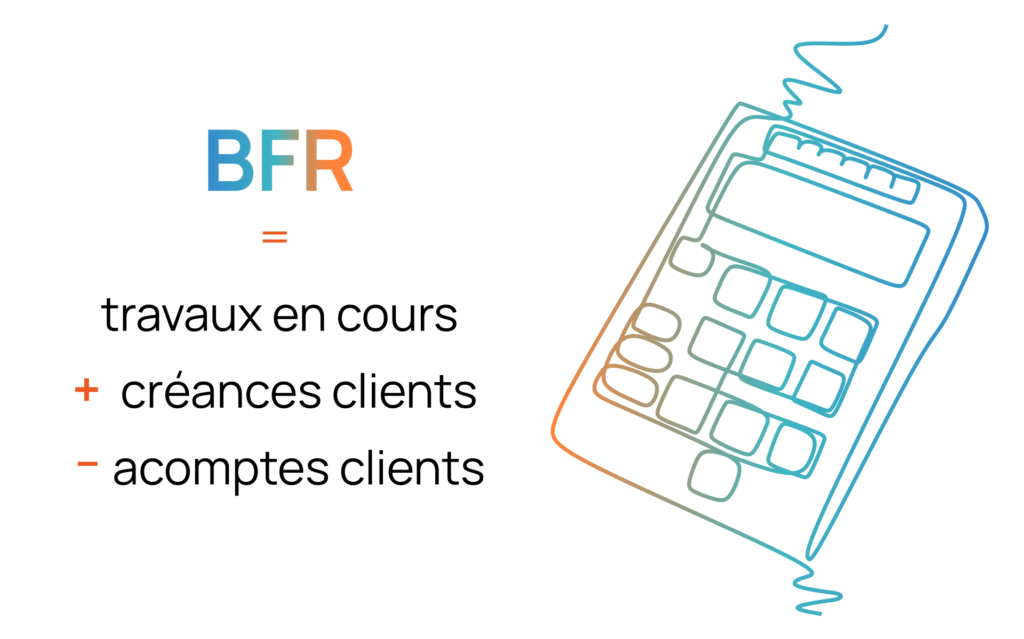
Why is BFR important?
The working capital requirement is a key performance indicator.
First, it highlights the financial reality of a company and its ability to generate CASH. It is for this reason that key partners such as suppliers or banks will make it a point of honor to scrutinize its evolution.
Then, the BFR is an important management tool since it foreshadows the evolution of the company’s cash flow . It reflects the management of inventories, trade receivables and suppliers outside of any equity contribution, additional bank loan or blocking of dividends to be distributed to shareholders.
Three interpretations are then possible:
- The BFR is less than 0: we no longer speak of working capital requirements, but of working capital resources. This means that there is enough cash to cover operating costs after settling the company’s debts to suppliers and pending settlement of creditors. The company even has a financial surplus which could, for example, be used to carry out external growth operations by self-financing.
- The WCR is equal to 0: the operating jobs are sufficient to cover the company’s expenses. There is no need for working capital, but the company also has no financial surplus and therefore no room for maneuver in the event of the unexpected.
- The BFR is greater than 0, which means that you pay your suppliers before being paid by your customers: there is therefore a difference in your cash flow between disbursements and receipts. This is not necessarily worrying, but to avoid a significant drop in cash, it forces you to find the amount necessary to finance your short-term cash needs (factoring, bank loan, recourse to equity, etc.).
Three methods to optimize your BFR
As you will have understood, having a BFR equal to or less than 0 allows your professional activity to operate more calmly and avoids having to resort to short-term debt which could deteriorate the financial health of your company. Thus, to optimize working capital, several levers exist. Just work on its components.
- Act on customer receivables to reduce the DSO or average customer payment time: the faster you collect your invoices, the more you reduce your WCR. The collection time for customers depends, among other things, on the profile of your customers, your commercial policy, your invoicing and dispute resolution processes (conditions and methods of payment granted, discounts, factoring, etc.). A defined, formalized and implemented credit management strategy is important to reduce late payments. If, despite everything, your company is facing unpaid bills, you can call on a collection company like GCE. Our collection agents identify disputes for you more quickly, negotiate payment with your debtors while preserving your commercial relations.
- Act on the supplier position to optimize the DPO or supplier payment period: for a good optimization, it is assessed in relation to the DSO, but also by taking into account the average payment period in the business sector of the company . To make the best use of your cash flow, one of the strategies will be to model your DPO on that of the sector average. Other means such as optimizing the pace of supply should also be considered.
- Act on stocks or DIO (inventory turnover rate): the faster the stock sells, the more your cash flow increases and the more your BFR decreases. Also, working in tight flow and reducing delivery times to avoid dormant stocks, obsolete or surplus products is an effective method to reduce BFR.
BFR, the indicator to control in the event of strong growth
It often happens that the upward trend in a company’s WCR is due to the growth of its activity. An increase in BFR is therefore not necessarily a bad sign . Indeed, the more the activity is important, the more the debts and the stocks increase. At the same time, customer payment terms have not necessarily changed. Indeed, the amount of sums to be advanced increases mechanically.
Let’s take a concrete example. When a company’s turnover is €730 million in year 1, the weight of a day’s turnover represents €2 million. If the turnover increases to reach 1,460 million euros in year 2, the weight of the turnover of one day increases to 4 million euros.
The receivables item which mobilizes the WCR, if it represents 20 days of turnover, will therefore weigh 40 M€ in year 1 and 80 M€ in year 2.
The main challenge is to control all the components of WCR over time, by building a real credit management policy, avoiding any drift on late customer payments for example, or by using financing techniques adapted to this situation. . .
In summary, your company’s WCR is an image of the financial reality of your company . If your BFR increases, many possibilities are available to you to help you optimize it to the maximum and thus relieve your cash flow. Contact us for more information.
